
The troposphere is the layer of the atmosphere closest to the Earth’s surface, and it is home to the majority of the Earth’s weather and climate systems. It is the layer where all of our weather takes place and it contains the majority of our atmosphere’s water vapor. There are many interesting facts about the troposphere that are important to understand in order to gain a better understanding of our planet’s weather and climate. This article will discuss some of the most fascinating and interesting facts about the troposphere. Read our interesting facts about Earths Stratosphere for more.
Uncovering the Secrets of Earth’s Troposphere: A Comprehensive Overview
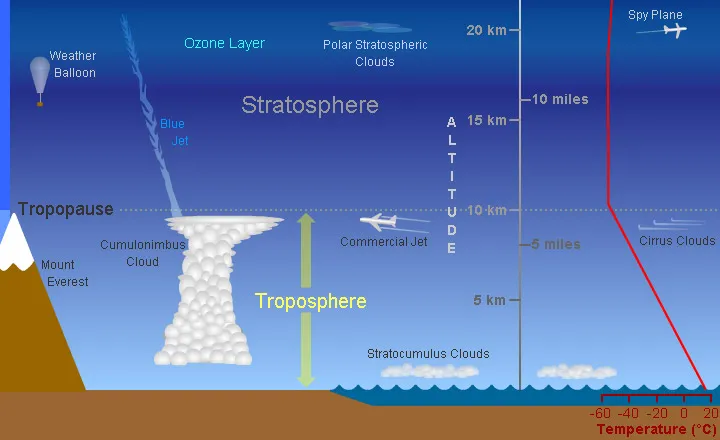
Earth’s troposphere is a dynamic and complex part of our atmosphere, responsible for the majority of our weather and climate conditions. It is the layer closest to the ground and is also the layer that contains the majority of our atmosphere’s water vapor and other gases. In this article, we will explore the secrets of the troposphere, discussing its composition, temperature, pressure, and the role it plays in our environment.
The troposphere is composed mostly of nitrogen (78%) and oxygen (21%). It also contains trace amounts of other gases, such as carbon dioxide and ozone. This layer of the atmosphere is kept warm by the sun’s energy and is important for regulating Earth’s climate. The temperature of the troposphere generally decreases with altitude, forming a layer of cooler air and clouds near the top.
The pressure of the troposphere is also significant. At sea level, the pressure averages about 1,013 millibars, but can vary depending on the weather system in the region. The pressure of the troposphere is also important for regulating the behavior of the air masses it contains.
The troposphere plays a vital role in our environment, providing energy and moisture for weather and climate. Through the process of convection, warm air rises and creates clouds and precipitation. This helps to cool the surface of the earth and redistribute moisture. The troposphere also affects the jet stream, which is responsible for transporting air around the globe.
Finally, the troposphere affects the way pollutants are distributed in the atmosphere. Certain pollutants are more likely to be trapped in the troposphere due to its lower pressure and temperature. This can lead to an accumulation of pollutants in certain areas, resulting in air pollution and health concerns.
In conclusion, the troposphere is an essential part of our environment, providing energy, moisture, and a means of transporting air around the globe. Understanding the composition, temperature, pressure, and role of the troposphere is important for understanding our environment and protecting it from the effects of pollution.
Exploring the Intricacies of Earth’s Troposphere: The Dynamics of Weather Patterns
The Earth’s troposphere is an intricate and dynamic system, which is responsible for a variety of weather patterns. From hurricanes to thunderstorms, the troposphere is the lowest layer of the atmosphere where a majority of weather takes place. It is characterized by a decrease in temperature with increasing altitude, and is home to a wide range of atmospheric phenomena.
The troposphere plays an important role in the generation of weather systems. Air currents originating from the warmer equatorial regions are known as Hadley cells, which move toward the poles and rise in the troposphere, cooling and eventually condensing into clouds. These clouds produce precipitation and create fronts that can then move into other areas.
The dynamics of the troposphere are further complicated by the Coriolis effect. This phenomenon occurs when air currents are deflected to the right in the Northern hemisphere and to the left in the Southern hemisphere due to the Earth’s rotation. This can create a variety of wind patterns, such as cyclones, which can influence weather in different parts of the world.
In addition to air currents, the troposphere is also home to a variety of other atmospheric phenomena. Thunderstorms occur when hot air rises quickly and forms a cumulonimbus cloud. This creates an area of low pressure, which draws in cool air from the surrounding area, leading to strong winds, heavy precipitation, and lightning.
The troposphere is an incredibly complex environment, and its dynamics are responsible for a variety of weather patterns. From thunderstorms to hurricanes, understanding the intricacies of the troposphere is essential for predicting weather and protecting ourselves from its potential dangers.
Understanding the Role of Earth’s Troposphere in Global Climate Change
The Earth’s troposphere is a layer of the atmosphere that plays a vital role in global climate change. Located just above the surface of the Earth, the troposphere is the most dynamic and active of the Earth’s atmospheric layers. It is responsible for most of the weather phenomena that take place on the planet, including the formation of clouds and storms.
The troposphere is also the main source of heat for the Earth’s climate system. This is because it absorbs and retains most of the solar radiation that is emitted from the Earth’s surface. This incoming radiation is then re-emitted in the form of infrared radiation, which is then trapped in the atmosphere by greenhouse gases. This phenomenon is known as the greenhouse effect, and it helps to regulate the Earth’s climate.
The troposphere also helps to regulate the movement of air around the planet. This is accomplished through several processes, including the convection of hot air, the advection of air masses, and the formation of atmospheric currents. These processes help to redistribute heat from the equator to the poles, which helps to even out temperatures around the world.
As global temperatures continue to rise, the troposphere is becoming increasingly important in the climate change equation. This is because the troposphere is more sensitive to temperature changes than other layers of the atmosphere. As temperatures rise, the troposphere is able to hold more water vapor and carbon dioxide, which can further amplify the effects of global warming.
In summary, the troposphere is a vital layer of the Earth’s atmosphere that plays a key role in global climate change. It helps to regulate the Earth’s climate by absorbing and trapping solar radiation, redistributing heat from the equator to the poles, and holding more water vapor and carbon dioxide as temperatures increase.
Leave a Reply